History
A 54-year-old female patient presented with severe back pain along with fever. An X-ray of the spine was inconclusive. Patient was referred for a 99mTc MDP bone scan to evaluate for spinal pathology. The image was acquired three hours after administration of 20 mCi of 99mTc MDP. Conventional 3D iterative and xSPECT BoneTM images were reconstructed and compared, along with fusion of CT and SPECT.
Findings
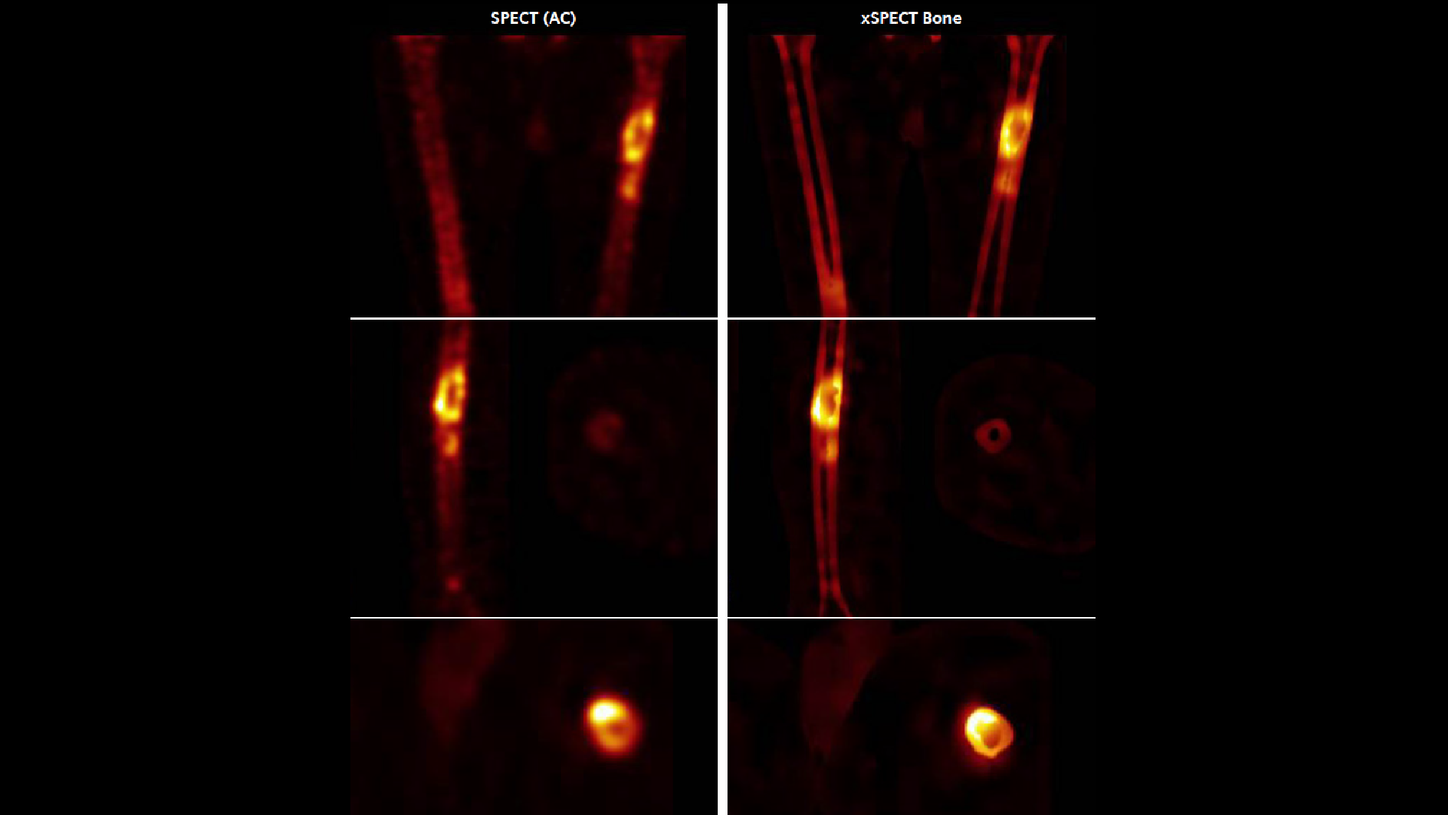
SPECT shows increased uptake of the tracer in the L3-L4 lumbar vertebral end plates and intervertebral disc. xSPECT Bone shows sharp delineation of the individual vertebrae with clear definition of the focal area of increased uptake within the L3-L4 intervertebral disc and adjacent vertebral end plates. xSPECT clearly defines the location of the uptake and delineates the sharp vertebral end plate margins, thereby demonstrating the narrowing of the L3-L4 intervertebral disc space as well as the tracer uptake within the disc. Other lumbar vertebrae show normal shape with normal intervertebral disc spaces without abnormal focal uptake.
Low-dose CT shows narrowing of L3-L4 intervertebral disc space with severe erosion of the adjacent vertebral end plates along with mild sclerosis. xSPECT and CT fused data shows increased uptake within the narrowed intervertebral disc space along with uptake limited to the zone of sclerosis adjacent to the vertebral end plate erosion. The other intervertebral disc spaces appeared normal without abnormally increased uptake or end plate changes on CT. Minor degenerative changes were visualized in the lateral aspect of L4-L5 vertebral end plates.
Comments
The clinical presentation of the patient, along with the SPECT (AC) findings of narrowing of disc space, end plate erosion, and severely increased bone metabolism within the disc space and in the adjacent vertebral end plates without major involvement of other intervertebral disc spaces, was suggestive of an intervertebral disc space infection. The intensity of end plate tracer uptake was clearly higher than the degree of sclerosis, which is also supportive of the diagnosis of active disc space inflammation. Subsequent to the diagnosis of intervertebral disc space infection, the patient was treated with intensive antibiotic therapy.
Conclusion
Compared to standard SPECT AC reconstruction, the xSPECT Bone images clearly delineated in the intervertebral disc spaces and uptake patterns and helped interpret the degree and extent of intervertebral disc inflammation and the correlation of uptake intensity to degree of erosion and sclerosis. This level of delineation with xSPECT Bone supported the diagnostic confidence of the interpretation of the study as a case of intervertebral disc space inflammation. Based on this diagnosis supported by xSPECT Bone, subsequent therapy decisions involving antibiotic administration were made.
Examination protocol
Scanner: Symbia™ with xSPECT Bone